


- COMMAND LINE MAC CHEAT SHEET ARCHIVE
- COMMAND LINE MAC CHEAT SHEET SOFTWARE
- COMMAND LINE MAC CHEAT SHEET PC
- COMMAND LINE MAC CHEAT SHEET FREE
For example, to run M圜ommandLineProg, use the following: To run a command in the current user’s home folder, precede it with the folder specifier. The list of known folders is stored in the shell’s PATH environment variable and includes the folders containing most command-line tools.įor example, to run the ls command in the current user’s home folder, enter the following at the command prompt, then press Return: Mac Terminal Commands Cheat Sheet If a command is located in one of the shell’s known folders, you can omit path information when entering the command name. In the Terminal app on your Mac, enter the complete pathname of the tool’s executable file, followed by any needed arguments, then press Return. An A-Z Index Of The Apple MacOS Command Line - SS64. Of course, that does come with a hefty price tag though, but it’s worth it if that passthrough charging feature is a must for your computing needs. OverpricedIf you're a loyal Apple superfan then you'll be wanting the official Apple USB-C adapter for your MacBook or MacBook Pro. You can use the command-line environment interactively by typing a command and waiting for a result, or you can use the shell to compose scripts that run without direct interaction.
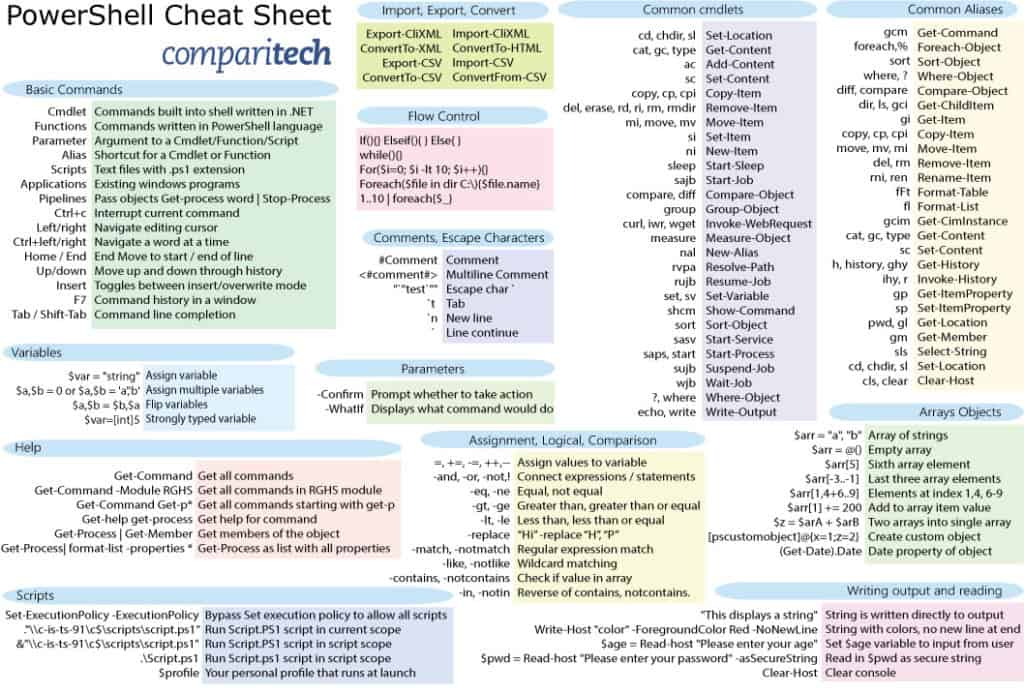
With it, instead of pointing and clicking, you type your commands and your Mac does your. Securely copy file1.Terminal (in your /Applications/Utilities folder) is the default gateway to that command line on a Mac. Securely connect to the system via SSH default port 22Ĭonnect to host via telnet default port 23ġ3) File Transfer scp file1.txt server2/tmp Ssh -p port_number connect to host using a specified port Search recursively for a pattern in a given directoryįind file names that begin with 'index' in /home folderįind files greater than 10000k in the home folder The command installs the binaries in the default/modified paths after the compilation The process may take some time, depending on your system and the size of the program It reads the Makefile to compile the program with the required operations. It will build the Makefile containing the instructions required to effectively build the project
COMMAND LINE MAC CHEAT SHEET SOFTWARE
configureĬhecks your system for the required software needed to build the program.
COMMAND LINE MAC CHEAT SHEET ARCHIVE
Performs an IP lookup for the domain nameĨ) Compression/Archives tar -cf home.tar homeĬreates archive file called 'home.tar' from file 'home'Ĭreates gzipped tar archive file from the source folderġ0) Install Source (Compilation). Retrieves DNS information about the domain Retrieves more information about a domain name
COMMAND LINE MAC CHEAT SHEET PC
Ping command sends an ICMP echo request to establish a connection to server / PC Sets rwx for owner, rw for group and everyoneĬhange owner and group owner of the directoryĭisplays IP addresses and all the network interfacesĪssigns IP address 192.168.0.1 to interface eth0ĭisplays IP addresses of all network interfaces Set rwx to the owner and r_x to group and everyone Set rwx permissions to owner, group and everyone (everyone else who has access to the server) Makes a process run with very low priorityĬhange file permissions of the file to octal Sends a signal to a process with its name Kills / Terminates all processes named proc Searches for the id of the process 'telnet' Prints the number of bytes, words and lines in a file Removes a directory forcefully and recursively Lists files - both regular & hidden files and their permissions as well. Used for changing / modifying user information
COMMAND LINE MAC CHEAT SHEET FREE
Total and Free memoryĭisplays information about system's hardware configurationĭisplays block devices related informationĭisplays free and used memory in the system (-m flag indicates memory in MB)ĭisplays PCI devices in a tree-like diagramĭisplays USB devices in a tree-like diagramĭisplays hardware information from the BIOSĭisplays the details of the active user e.g. Displays how long the system has been running including load averageĭisplays the current calendar month and dayĭisplays currently logged in users in the systemĭisplays more information about CPU e.g model, model name, cores, vendor idĭisplays more information about hardware memory e.g.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
